What is a Cool Roof?
Roofs are essential when it comes to the efficiency of a building. As you can imagine, a building’s roof is hit by direct sunlight throughout the day. A cool roof’s design reflects a majority of sunlight, making it an ideal insulator. The color of a roof largely determines the amount of light a roof can absorb. Similar to how light-colored clothing keeps you cool on a sunny day, light-colored shingles help keep a structure cool. In fact, dark-colored roofs can quickly become 50 degrees hotter than their lighter counterparts, according to Energy.gov. Wood shingles are naturally light-colored, but you can choose a conducive color with any roof material. Also, low-sloped roofs (<17°) tend to absorb more direct radiation on summer days. So, a steep-sloped roof (> 17°) is a natural option to keep a roof cool.
Most manufacturers have cool roof shingle options. Reflective asphalt shingles are made with reflective granules and look nearly identical. Cool roof options may also utilize specialized liquid or aluminum coatings on their exteriors to reflect heat. This type of glazing is synergetic with certain types of roof materials such as clay tiles, concrete tiles, and metal shingles. Another type of cool roof design employs layers of reflective sheets underneath the tiles with a smooth finish on the outermost layer, to reduce surface area. The Cool Roof Rating Council is responsible for testing and rating roofing products. All in all, a cool roof improves energy efficiency by reducing the amount of heat that can enter a building.
Solar Reflectance
Solar reflectance refers to the ability of a material to reflect light. It’s measured from 0 to 1; the higher the value, the more light is reflected. Keep in mind we are talking about visible light. Light and heat are correlated, but not the same thing. Imagine a white panel laying next to a black panel. White has higher reflectance and may get warm, but it will also reflect light back into the atmosphere. The average solar reflectance rating is .10 for a typical roof, which equates to 10%. Contrarily, a cool roof has a of 20% reflectivity or higher.
Thermal Emittance
On the other hand, thermal emittance is the amount of heat radiation an object can absorb. Heat is a phenomenon that can be felt rather than seen. Measured from 0 to 1, the lower the value the less heat transfer occurs.
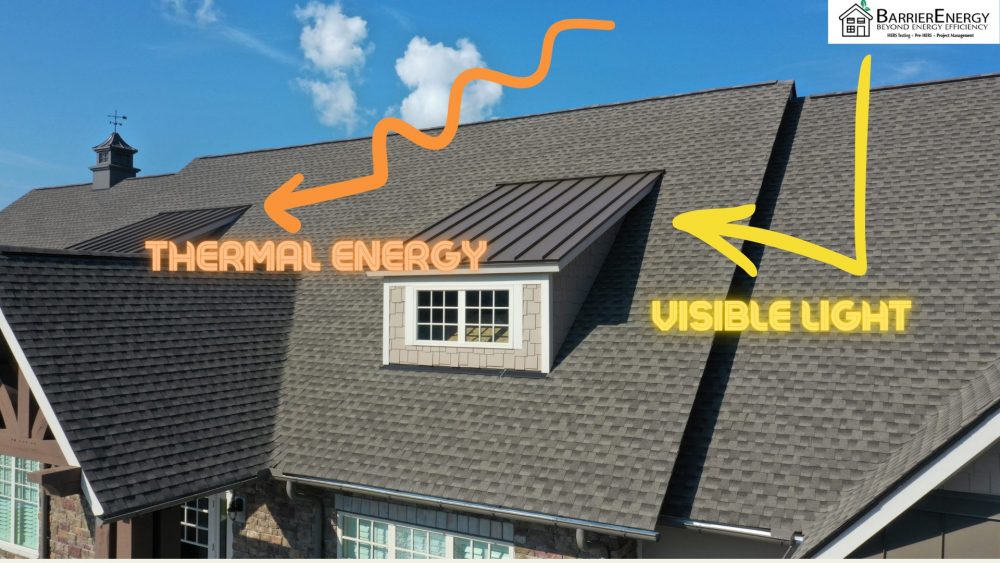

Solar Reflective Index (SRI)
Overall, the temperature of the roof is based on a combination of solar radiation, surface reflectance, and emittance. The Solar Reflective Index indicates a combination of all three measurements. The index is a scale of 0 to 100, with 0 being the equivalent to black and 100 being the equivalent to white. You can locate an SRI calculator on the California Energy Commission’s website by clicking on Worksheets > 2019 SRI Calculator Worksheet. SRI is used when verifying cool roof requirements.
Cool Roof vs. Radiant Barrier
What is a Radiant Barrier?
Installers place radiant barriers inside attics, as opposed to on the exterior roof itself. Essentially, the barriers consist of a highly reflective foil that is mounted to the underside of the roof. They are designed to provide a boundary between the exterior sun and the interior space by dispersing radiant heat. A designer could specify insulation on the underside of the roof as another alternative option. Both can achieve a similar result, which is to stop heat transfer at the source.
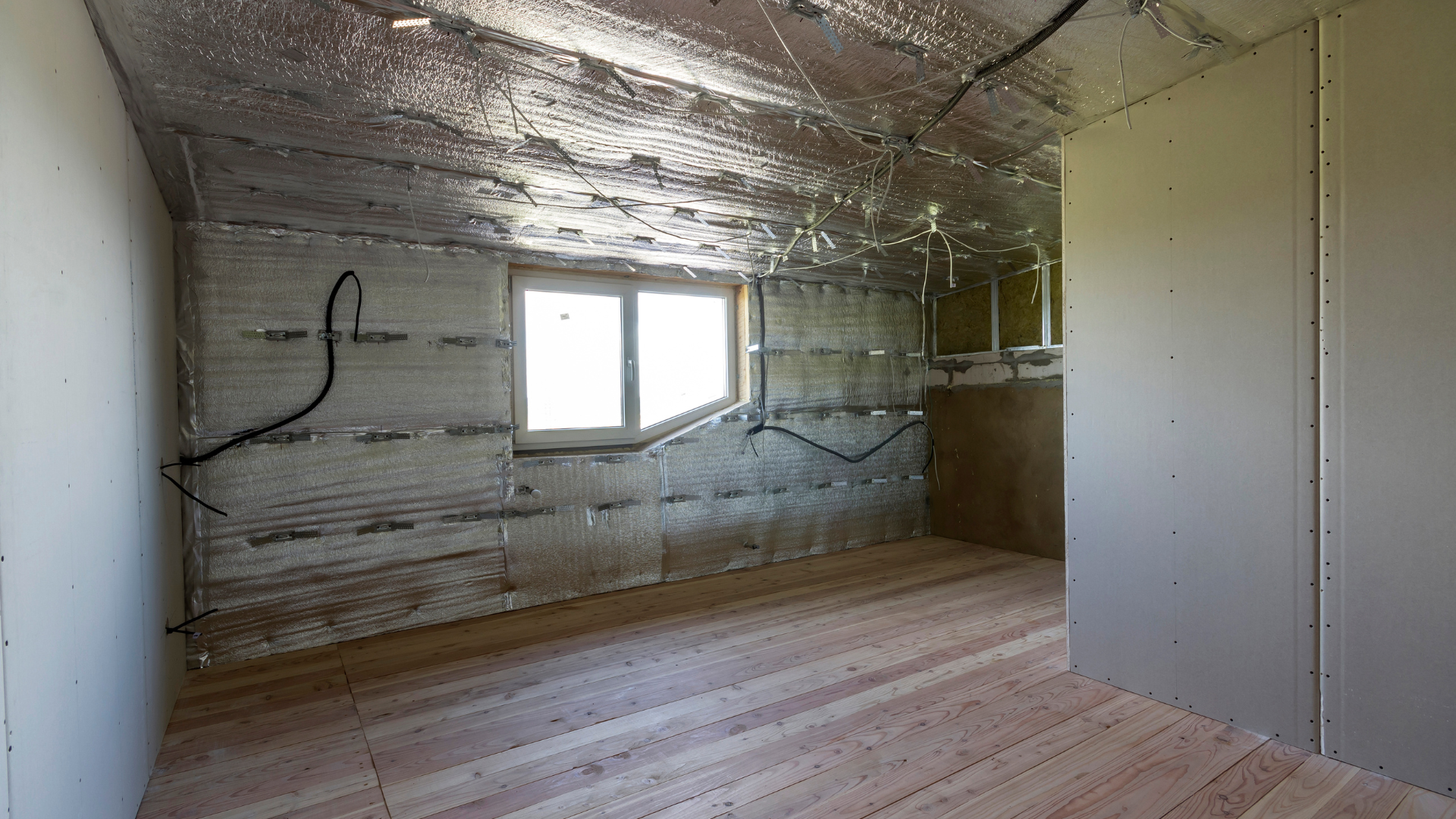

The Benefits of Efficient Roof Designs
Both radiant barriers and cool roofs share a common goal, to reduce energy waste. These energy-efficient designs have a plethora of advantages. Firstly, you are reducing your energy bills and HVAC loads by reducing unwanted heat transfer. Especially in California, this is crucial because of utility shut-offs and electricity rate increases at peak times of the day. Secondly, they improve comfort by allowing greater temperature control. Not to mention the heat-related illnesses that these products can avoid in emergency situations without power.
Thirdly, efficient roofs prevent the deterioration of roofing materials and thusly maintenance. Think of all that roofing you’ll save from landfills while you get to fill your wallet! Lastly, they reduce pollution by association with efficiency. Did you know that urban areas can experience higher air pollution due to a bubble effect of higher temperatures from reflective infrastructure? Not only do they reduce greenhouse gas emissions, but they also reduce this heat-island effect. If you are a property owner or builder, you should be highly interested and radiant barriers and cool roofs. As a result of efficiency, they will help keep your property pleasant and aerated, especially during hot summer months.
Title 24 Cool Roof and Radiant Barrier Requirements
Your construction project may require a cool roof or radiant barrier. Therefore, you’ll need to consult your Title 24 report. If required, a HERS Rater will fill out an installer verification form to prove compliance. Locate Title 24 requirements within your approved plan set. If you need assistance with this, request help from your Title 24 consultant or the company in charge of installer verifications. Luckily, that is our job here at BarrierEnergy!
When choosing materials, make sure to read the specification sheets thoroughly to assess that their efficiency ratings match the plans. Here is a link to the official cool roof directory straight from the Cool Roof Rating Council.
Title 24 Cool Roof Requirements in the 2019 Building Code
Your Title 24 document, also known as the CF1R, outlines the envelope requirements for your project. Review it in order to find the minimum efficiency specifications the designer selected for compliance. For example, all new single-family residences and some high-rise or commercial buildings must meet a minimum thermal emittance of .75.
Specifications depend on the climate zone, framing material, building type, and roof slope. The contractor must model the roof to reflect the proposed construction, or else the project may risk falling out of compliance. In some cases, there are exemptions for using high R-value insulation on the roof underside, installing solar panels, or adopting certain construction materials. Additions of 300 sq ft or less are exempt from the cool roof requirement.
Title 24 Radiant Barrier Requirements in the 2019 Building Code
A radiant barrier could be prescribed instead of or in addition to a cool roof, depending on the climate zone and building type the construction is in. All radiant barriers must have a thermal emittance of at least .05. For low-rise residential single-family and multifamily buildings with ducts and air handlers located in the conditioned space and additions greater than or equal to 700 square feet, a Title 24 document will require a radiant barrier (Climate Zones 2-15).
Along with radiant barriers, attics are required to have a vent high fraction of at least 0.3. Vent fraction is the percentage of vent area compared to the size of the attic. That’s something you’ll want to find out or talk with your architect about during the design phase.
Title 24 Requirements for the 2022 Building Code
Every three years, the CEC improves previous codes. Typically, regulations get more strict with each code cycle. Whichever year with the building department approved your permit determines the code cycle that applies to your project. Since there were not many alterations made to the category of roofing, we can lump listen to one section. For 2022 code requirements I will direct you to the Energy Code Ace 2022 Reference Tool. Search for “radiant barrier” or “cool roof” in the upper left-hand search bar for information on Mandatory Requirements for Insulation, Roofing Products, and Radiant Barriers.
To learn more about title 24 requirements in California, subscribe to our blog. Or, feel free to contact us with questions, comments, and concerns.


Recent Comments